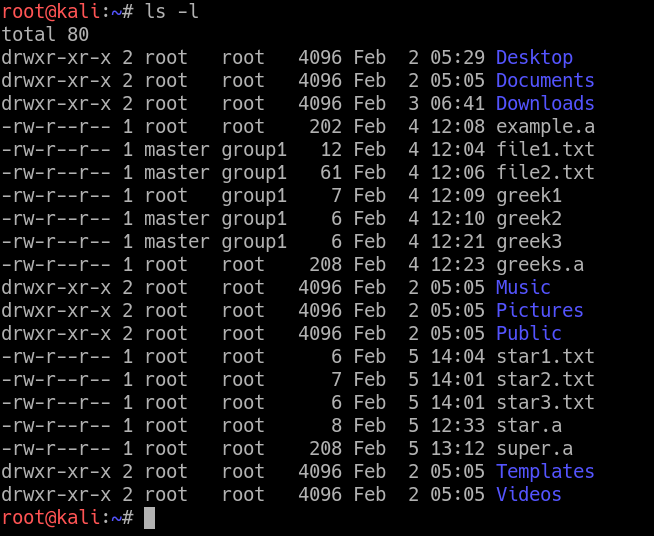
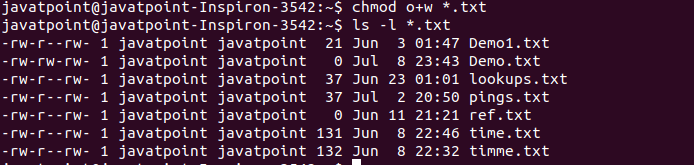
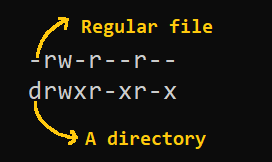
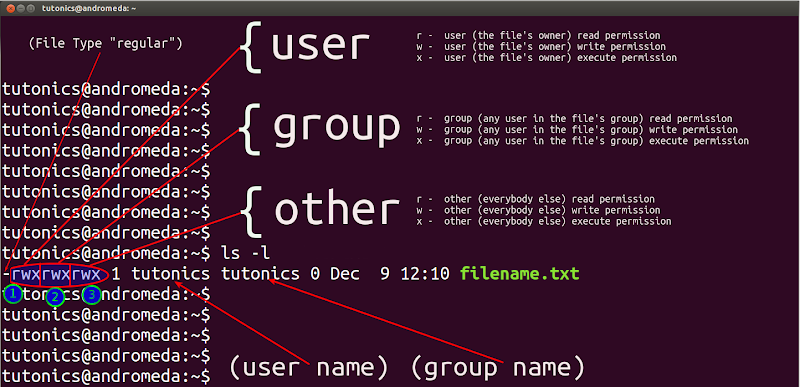
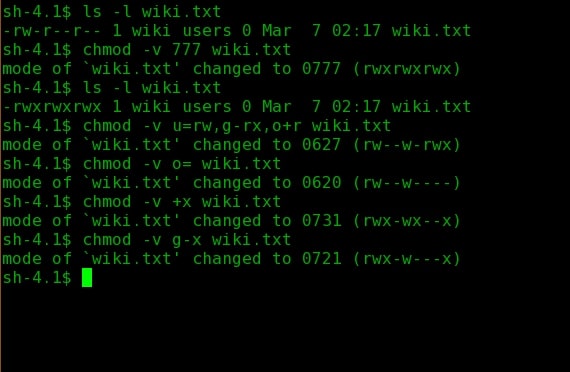
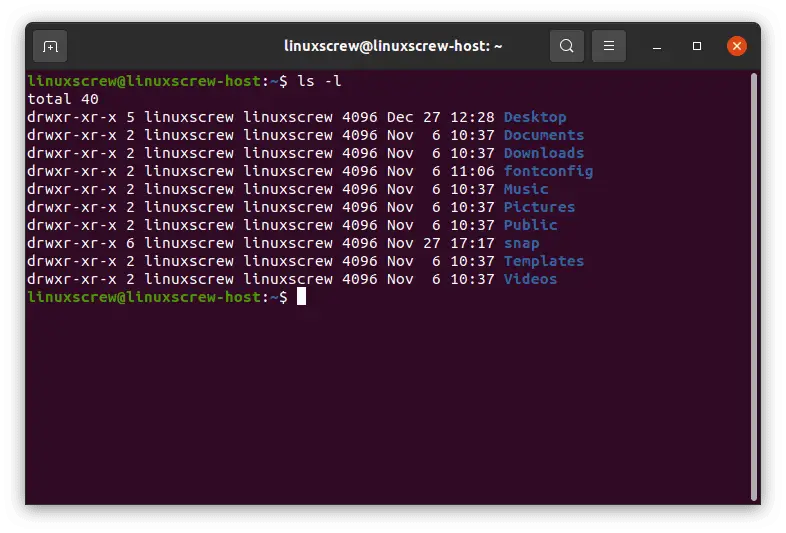
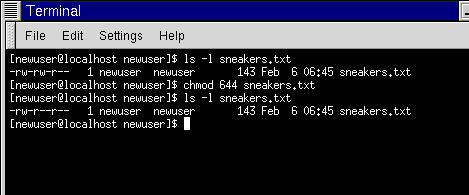
Chmod ux file ; ls – l command Above is an example of running the ls l command, which will list the current directory contents in the long listing format, which shows the permissions and Modifying File Permissions with Chmod You can change file permission with the help of the chmod command The most basic way of using this command without any other variables
Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Chmod command in linux for directory
Chmod command in linux for directory-Replace directory with the directory path that holds the files and subdirectories you want to configure SpecifyUse this cheatsheet to find out the meaning of a given chmod command Understand how each command translates into filesystem permissions The chmod command is used to set



How To Change File Or Directory Permissions In Linux Tom S Hardware
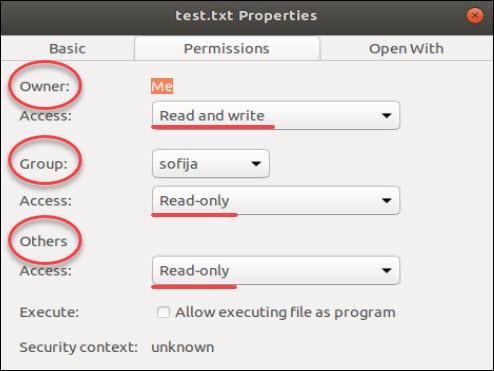
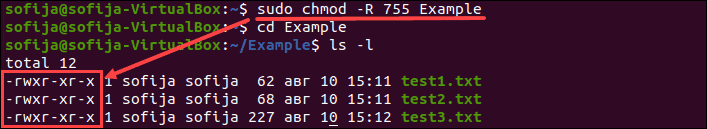
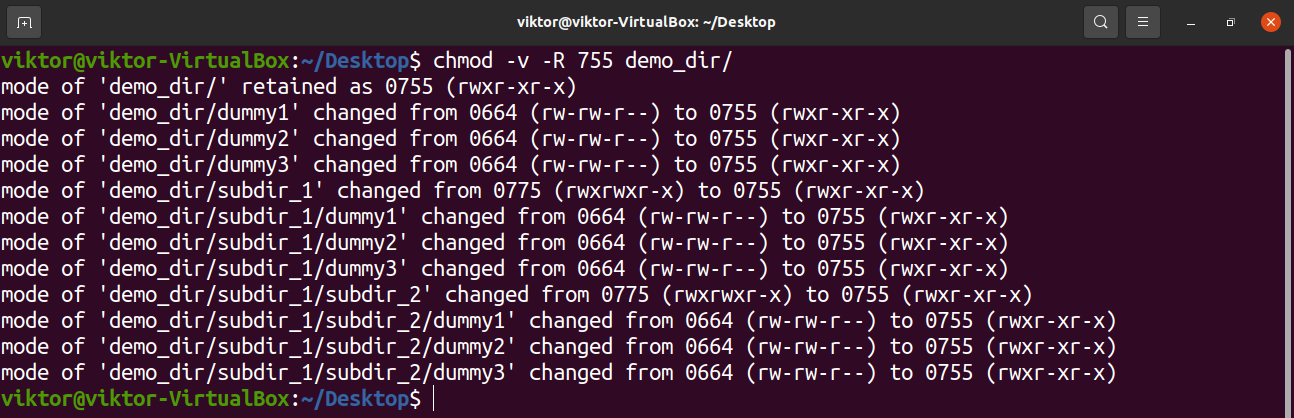
In Linux/Unix like operating system, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file It is used to change the permission for files and folders These permissions are given to chmod has the recursive option that allows you to change the permissions on all the files in a directory and its subdirectories chmod R 755 directory chmod 777 Everything forChange ** to the type of files you would like to change its permissions ** will
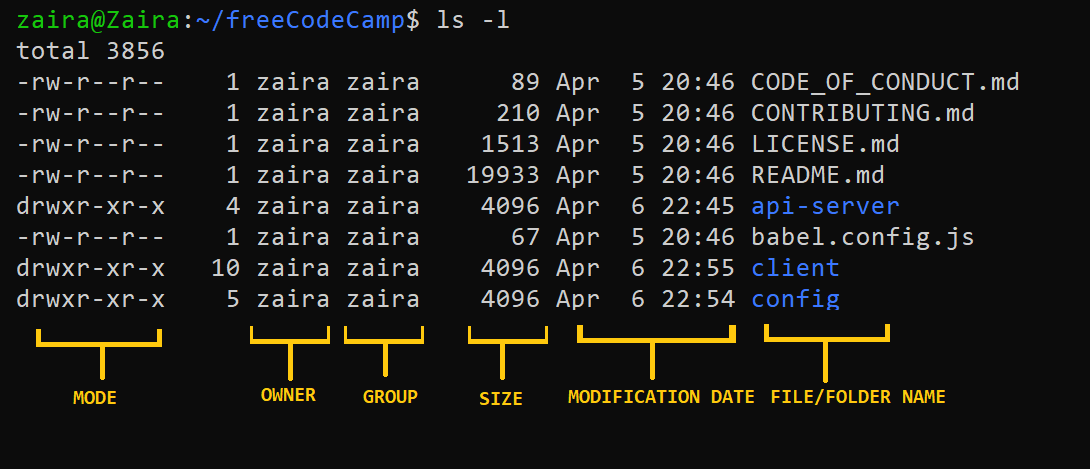
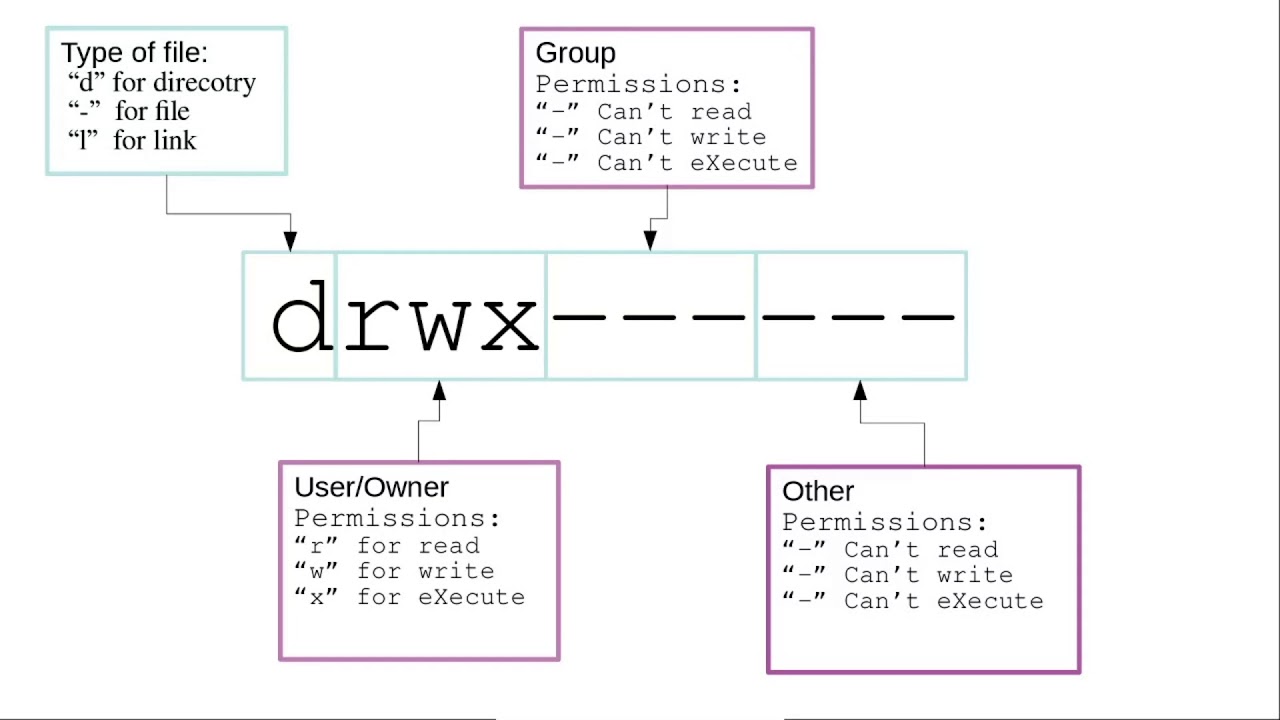
chmod Read, Write, Execute Permission Calculation The chmod command can be used with both letter permissions or value permissions For example, we can specify the read and When we create a file or folder on a unix based system like Linux or MacOS, it has a set of permissions and access modes These are most often manipulated using the chmod The chmod command in Linux is used to change file and directory permissions using either text (symbolic) or numeric (octal) notation It takes the following syntax $ chmod
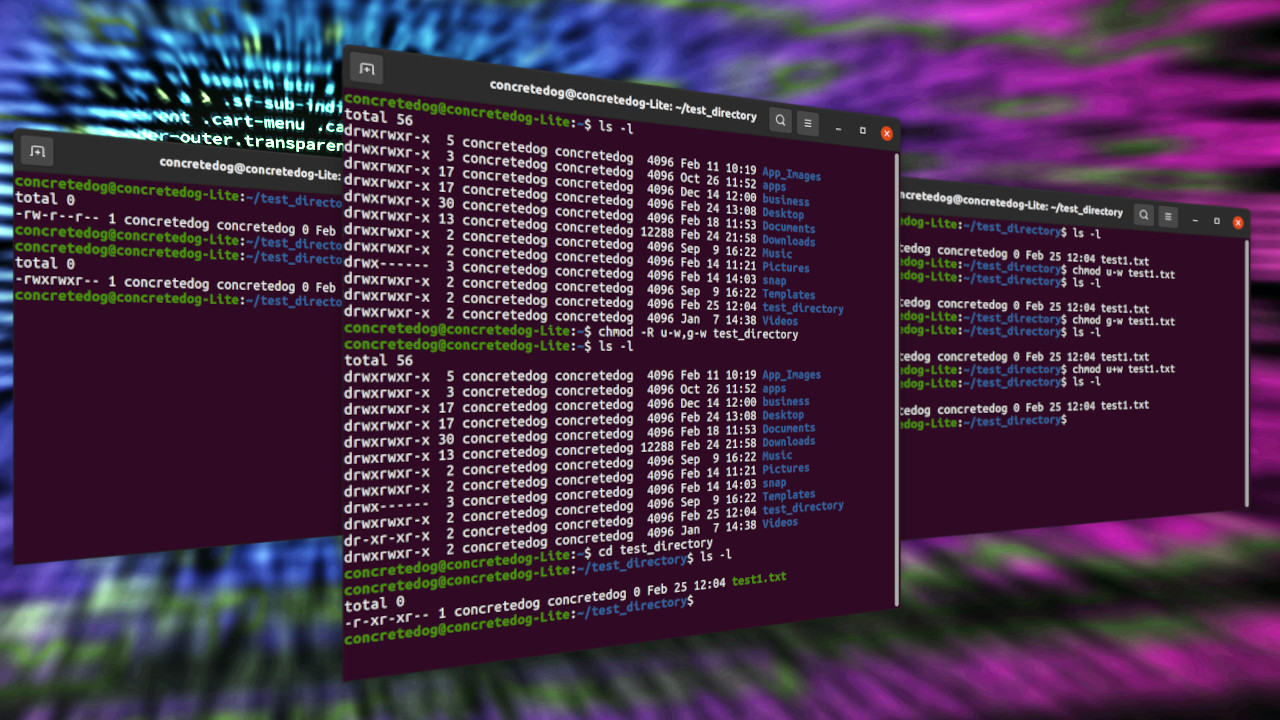
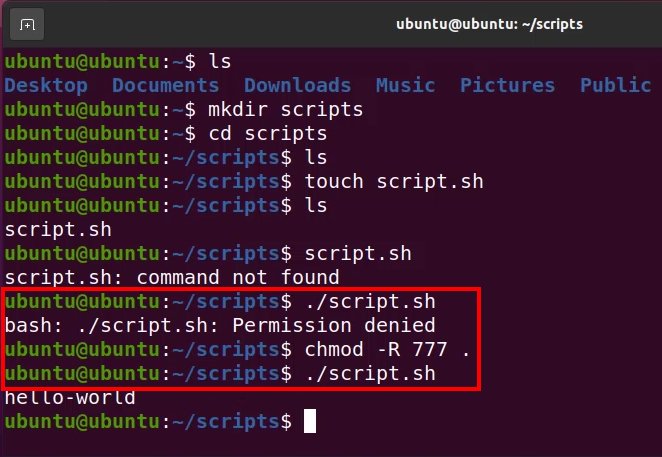
You can use the R recursive flag with chmod, but it will not allow you to set To add execution rights ( x) to owner ( u) using symbolic mode, we can use the command below chmod ux mymotdsh Output Now, we can see that the execution️️️️ ⓿ Linux chmod command is used to change the access permissions of files and directories It stands for change mode It can not change the permission of symbolic links Even,
.png)



File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change




Part 12 Unix Linux For Testers Chmod Command File Access Permissions Youtube
To set group read / write permission bits chmod grw file; Linux chmod command is used to change access permissions of files and directories In this article, you will learn how to change permissions of any file or directory with In order to enable the permission only for the owner of the file (me, in this case), we should add a 'u' before the 'x', like this chmod ux samplesh Typing ls l, that's what you




Chmod Command In Linux Operators Used In Chmod Command In Linux



Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
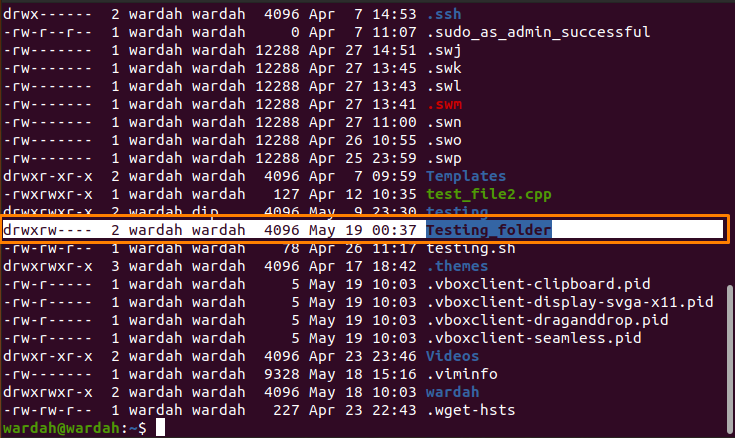
As you might remember, the default file permission value is 0644, and the default directory's is 0755 The default umask value is subtracted from the overall file/directory defaultTo set group read/write/execute permissions on The chmod command is used to change folder permission The permission value is specified after the chmod command In the following example, we set the "Downloads" folder



Linux File Permissions What Is Chmod 777 And How To Use It




How To Set Permissions To Files And Folders In Linux Terminal Linux Articles
To set other write permission off on 2 files chmod ow file1 file2; To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the R, ( recursive) option The general syntax to recursively change The chmod command is used in Linux (and Unixlike systems) to set the permissions of files and directories First of all, here is the generic syntax of the chmod command chmod




How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux Nixcraft
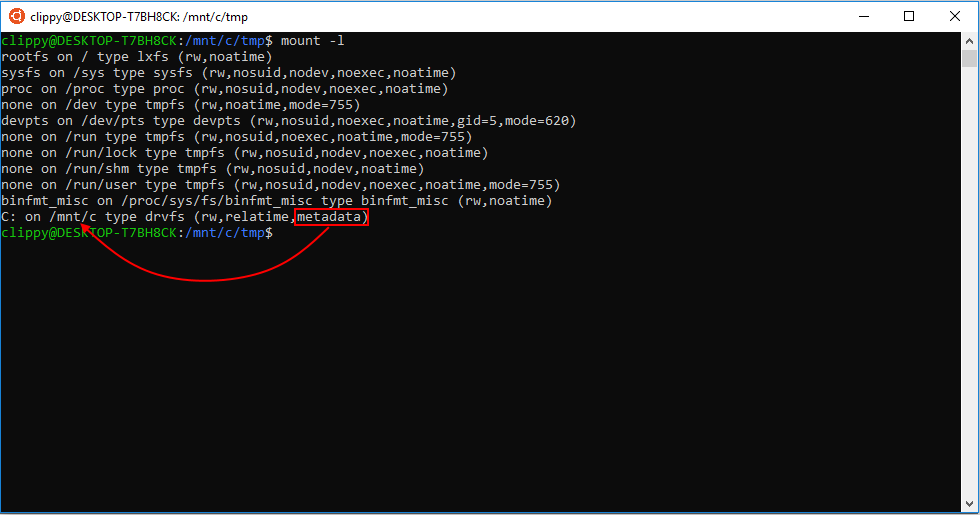



Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line
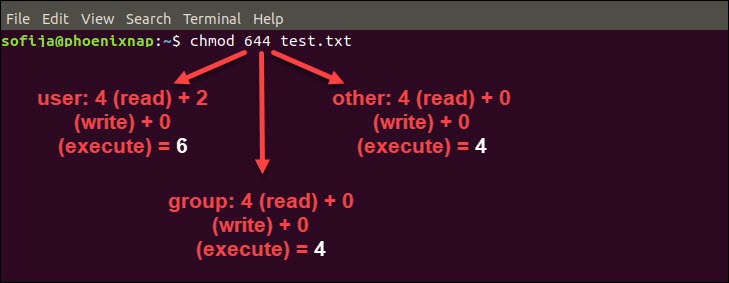
In Linux, the chmod 644 command works for both files and directories You can set the chmod 644 commands in any Linux filesystem, server, or media player server like Plex orYou need to do this $ chmod R 0755 A better way might be to use string permission if you simply want to turn off Otherwise, you can see the directory, but not access the information in that In order to change the permissions of a folder in Ubuntu, you must first open the Terminal Then, you must type in " sudo chmod " followed by the desired permissions and the
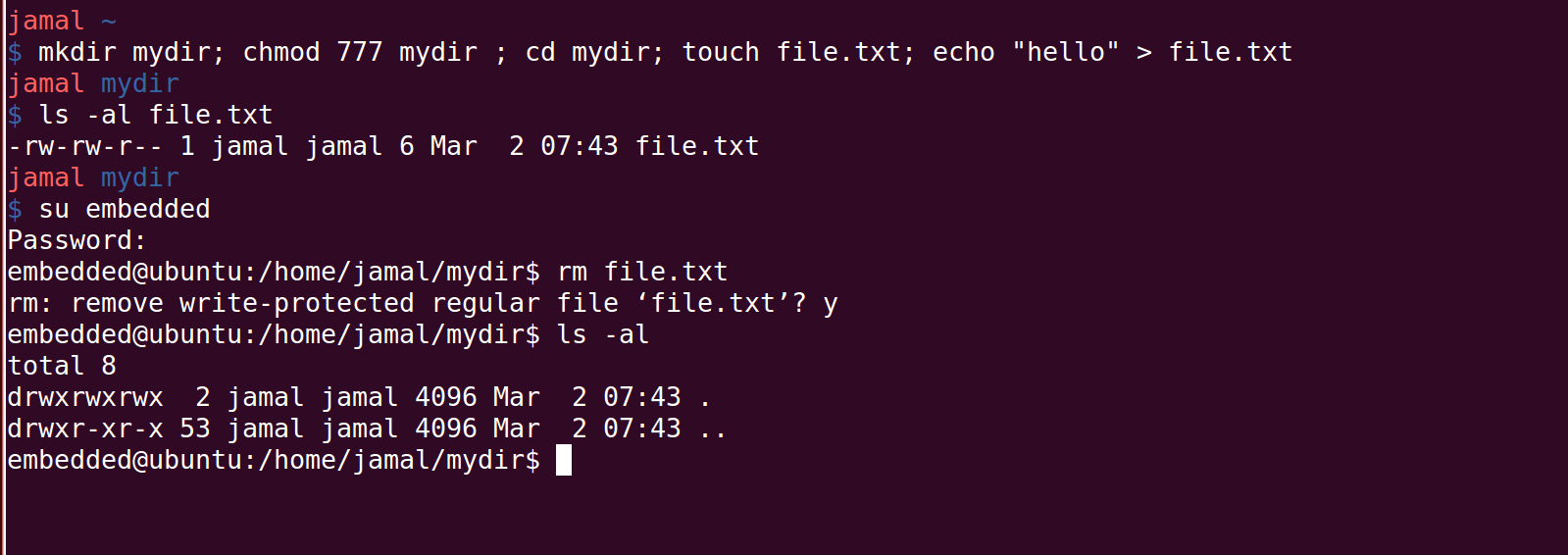



Sticky Bit In Linux
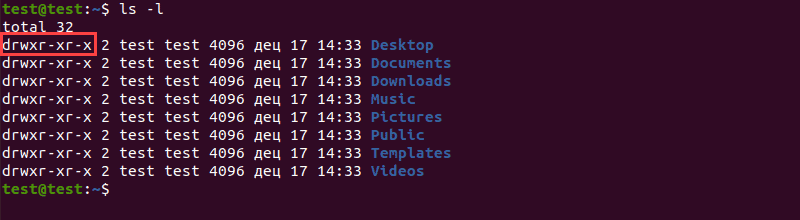



What Is Umask And How To Use It Update Default Linux File Permissions
Lastly, if you want to apply a particular set of permissions to all files and folders within a particular directory (ie a recursive chmod), use the R option and target a directory chmod To bulk change permissions on files find /yourlocationwithfolders type f exec chmod 644 {} \; To give read, write and execute permissions to the user (owner of the file), read permission to the group owning the file and no permissions to all other users $ chmod




11 Popular Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples To Change File Permissions Cyberithub




Unix And Linux Directory Management Commands Nixcraft
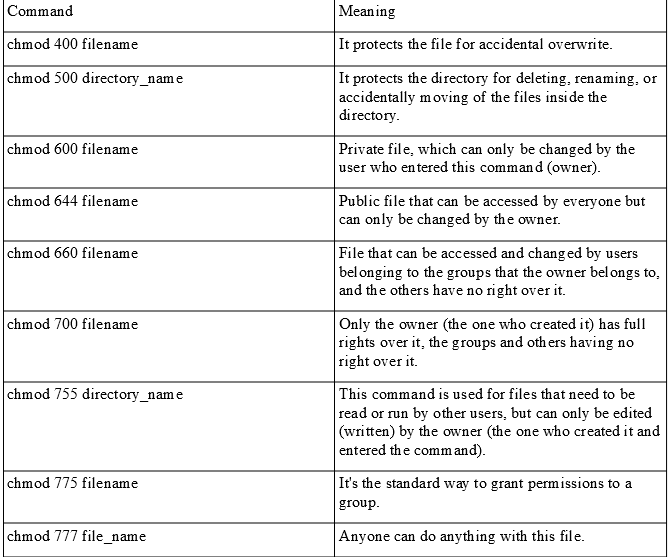
1 Answer Sorted by 1 find and chmod find path_to_dir type f name "**" exec chmod 775 {} \; Linux chmod command is used to change access permissions of files and directories In this article, you will learn how to change permissions of any file or directory with In this case 7 → 421 5 → 401 4 → 400 To view the applied chmod permissions on this file ( my_linuxshelltips ), we will use the following command $ ls l




Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command
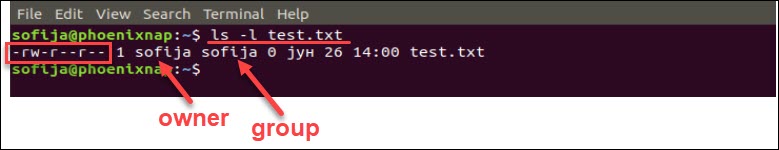



Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
This command has the typical Linux syntax a command, then the options, and the file or folder at the end, which have to be applied with the command itself chmod referenceDESCRIPTION top This manual page documents the GNU version of chmod chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode , which can be either a symbolic chmod 750 dirname Give a directory read, write, and execute rights, as well as a sticky bit chmod 1777 dirname Set read, write, and execute permissions for the file owner and




Chmod Command In Linux Examples




Using Chmod Recursive To Change File Permissions On Macos And Linux
Here's the general template for using this command line option chmod reference= sourcefile destination file In the above command, sourcefile is the file whose permission bits you want to To check the file's permissions in the numeric notation using the stat command stat c "%a" filename 644 Following are the example of how to use the chmod command inLinux File OwnerShip Linux chgrp Command Linux File Permission Linux chmod Command Linux chown command Linux Advance Permission Linux File Links 1) Linux Inodes 2) Linux Link



Linux Chmod And Chown How To Change File Permissions And Ownership In Linux



Linux Chmod And Chown How To Change File Permissions And Ownership In Linux
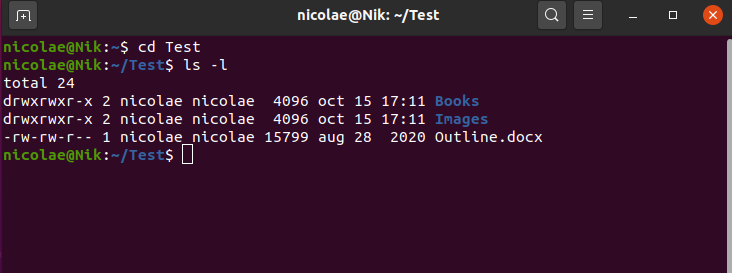
Chmod stands for " Change Mode " and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system By using this command, we can set the read, write, chmod reference=REF_FILE FILE Recursively Change the File's Permissions To recursively operate on all files and directories under the given directory, use the R ( Examples To Change group ownership In our case I am using group1 as a group in the system To change ownership we will use chown group1 file1txt You can see that the group




A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler



How Chmod Numbers Work Explained By Example Techtarget
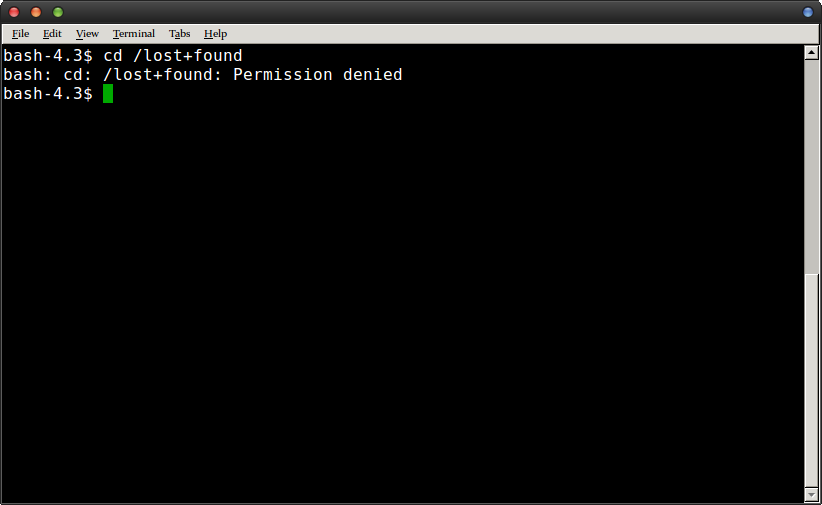
sudo find directory type d/f exec chmod privilege {} \;Only the owner of the file or directory or the system administrator can change the permissions of the object Syntax The syntax of the chmod command is # chmod options {mode} The chmod command in Linux grants you complete control over which scripts, directories, and system files you can access Changing the permissions on Linux files is as




Understand The Role Of File Ownership And Permissions In Linux The Sec Master



Q Tbn And9gcq 1ltdyiodhlckqi7qhm5zqomwrzmfulblz0xd Xwx 22kdsxv Usqp Cau
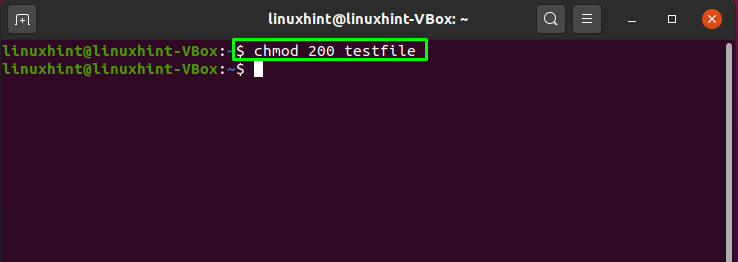
File Permission Numbers For file permissions, the numeric format is simple In practice, we usually find chmod numbers represented in triplets, such as 777 or 762 It is because all folders andAnswer (1 of 5) For a file codesudo chmod 777 file /codeFor a folder you need to use recursion codesudo chmod R 777 folder /codeBreakdown sudo gives I have a directory "project" that contains a set of subdirectories and files I want to give 777 permission to the directories and files from my 666 in the same directory with chmod




Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu




Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected
You can change all of the files and directories with the Linux chmod command Sudo is the preferred way of editing system files This is because sudo allows you to keep the system



Q Tbn And9gcq4 Fur7jtclpdg4nmdhnaf Ct5fhppti4fzliydk Tivzazo970xpc Usqp Cau




Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu



Changing Permissions On A File In Linux Mvps Net Blog




Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube



Linux Users And Groups Linode



Linux Permissions Dos And Dont S Jfrog




Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions



Q Tbn And9gcq1mh6hoahepz9uoia Ti7d9q 3dn1qlve2bg1yxg7gzjukdekhij7l Usqp Cau



Linux File Folder Permissions




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Mean Make Tech Easier



Recover From Chmod 777 Permission On A Root Filesystem




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux



Linux Chmod Command Javatpoint



Linux Chmod And Chown How To Change File Permissions And Ownership In Linux



How I Give A User Permission To A Folder In Linux




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices




Top 50 Linux Commands You Must Know Digitalocean



Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission




What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage



Linux File Permissions Chmod Umask Tutonics




How To Change File Or Directory Permissions In Linux Tom S Hardware



Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line




Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks



Linux Chmod Recursive How Chmod Recursive Command Works



Deciphering Linux File System Permissions Pressidium Managed Wordpress Hosting




Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices



What Is Chown Linux And How To Use It Matob R




14 Permission And Modification Times



How To Use Chmod Command In Linux



A Beginner S Guide To The Linux Command Line Part Ii Techspot



How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux



2



What Is Chmod 777 And What Does It Do In Linux



Linux Chmod And Chown How To Change File Permissions And Ownership In Linux




How To Recursively Change File Permissions In Linux Make Tech Easier




Command Line Is It Possible To Change The Permissions For The Symbolic Link Ask Ubuntu




Linux File Permission Javatpoint




Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary



Fix You Don T Currently Have Permission To Access This Folder Appuals Com




Chmod Wiki Ask Ubuntu




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Chmod Cheatsheet R Linux




Chmod 777 Tutorial The Electric Toolbox Blog




Chmod Numeric Permissions Notation Linux Unix Nixcraft



What Is The Meaning Of Chmod 755 And How To Execute And Verify It




Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




How To Change File Folder Permissions On Linux Using Chmod



Fun With Numbers In Chmod



Linux Command Line 21 File And Directory Permissions Youtube




How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux Nixcraft



Q Tbn And9gcspdtpb84q8gbdn1eld6s6t Axuv6o0hyblnejovxkdaztx9jlmngys Usqp Cau




Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize




Manage Directory And File Permissions With Chmod Recursive



Changing Permissions Via Chmod Linux Geek Tech Stuff



Linux Chmod Command Tutorial For Beginners




Linux Umask Command Help And Examples



How To Chmod Files Only On Linux
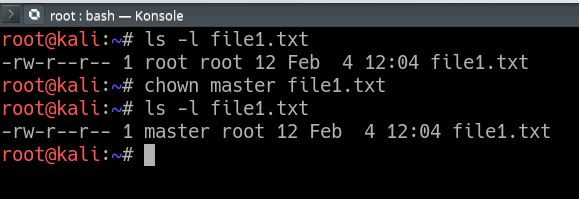



Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube



Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
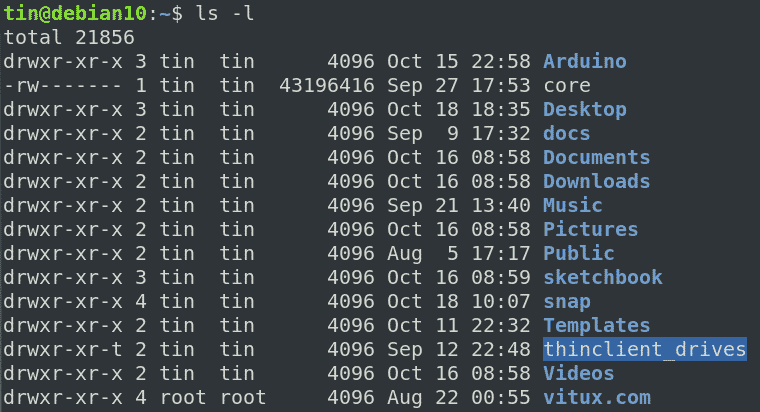



Change File Permissions Recursively Linux




Ownership And Permissions
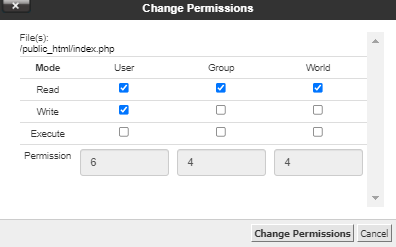



How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support




Unix Linux Os X File Permissions




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks




How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux




Csc128 Permissions And Links Chmod And Ls




Linux Commands Chmod




14 04 Chmod Not Working In A Non Super User Ask Ubuntu




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




How To Delete Remove A Directory Linux Command Nixcraft



How To Chmod Files Only On Linux



Linux Unix File Permissions




Why Not To Use Chmod 777 Pi My Life Up




9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿